Instructions for using the utility to calculate pipe size according to flow rate
One of the most renowned methods of pipe sizing is using the Hazen-Williams equation, especially when the fluid involved is water.

The equation estimates the frictional loss (feet) for a specific pipe with Length, L (feet), Diameter, D (inch), Flowrate, Q (usgpm) and C-value: Hazen-Williams coefficient, C.
The C-value of different materials of pipes can be referenced from various sources, which are summarized below. The higher the C-value, the “smoother” the flow in the pipe.
| TYPE OF PIPE/LOẠI ỐNG | C VALUE/ GIÁ TRỊ C |
|---|---|
| General Metal (Extremely smooth) - Ống kim loại tổng hợp cực nhẵn | 130 |
| Cast Iron (CI) - Ống Gang | 100 |
| Cast Iron Cement Lined (CICL) - Ống gang lót xi măng | 130 |
| Cast Iron Bituminous Lined (CIBL) - Ống gang lót Bitum | 130 |
| Cast Iron (Asphalt Coated) - Ống gang (phủ nhựa đường) | 100 |
| Ductile Iron (DI) - ống gang dẻo | 110 |
| Ductile Iron Cement Lined (DICL) - Ống gang dẻo lót xi măng | 130 |
| Mild Steel (MS) - Ống thép nhẹ | 120 |
| Mild Steel Cement Lined (MSCL) - Ống thép nhẹ lót xi măng | 130 |
| Galvanised Iron (GI) - Ống sắt mạ kẽm | 120 |
| Stainless steel - Ống inox | 140 |
| Steel - Ống thép | 100 |
| Steel (Corrugated) - Ống thép tole | 60 |
| Copper (Cu) - Ống đồng | 140 |
| Aluminium (Al) - Ống nhôm | 130 |
| Brass (Br) - Ống thau | 130 |
| Lead - Ống chì | 130 |
| Tin - Ống thiếc | 130 |
| Corrugated metal - Ống kim loại tole quấn | 60 |
| Reinforced glass fibre (FRP) - Ống composite | 140 |
| Plastic (General) - Ống nhựa tổng hợp | 130 |
| High-density polyethylene (HDPE) - Ống HDPE | 150 |
| Acrylonite Butadiene Styrene (ABS) - Ống nhựa ABS | 130 |
| Polyethylene (PE) - Ống nhựa PE | 140 |
| Polyvinyl chloride (PVC, CPVC) - Ống nhựa PVC, CPVC | 150 |
| Spun Cement - Ống xi măng ly tâm | 130 |
| Concrete - Ống bê tông | 100 |
| Vitrified clay - Ống đất sét thuỷ tinh | 110 |
| Wooden - Ống gỗ | 110 |
| Masonry - Ống xây dựng | 110 |
| Glass - Ống thủy tinh | 130 |
We can use the Hazen-Williams equation to estimate pipe sizes D, required for a given pipe C-value, flowrate Q, and the allowable frictional loss over a fixed 100 feet length of pipe (30m). This “ft/100ft or m/30m” maximum allowable friction loss is commonly set in the range within 4 to 10ft/100ft (1.2 to 3m). 4ft/100ft means that 4 feet of loss is the maximum that can be accepted in our design per 100 feet run of pipe. This value is then referred in a pipe size chart as shown below.
Instructions for using the pipe size calculation utility with images
Utility interface:
Water Pipe Size Calculator
| Unit | ||
|---|---|---|
| Types of Pipe | ||
| C-Value of Pipe (Hazen-Williams coefficient) | ||
| Flowrate | M3/H | |
| Maximum Allowable Frictional Loss From 1,2 to 3,0. The smaller the pipe diameter, the higher this loss, value 1.2 is the average allowable value. | m/30m dài | |
| Min. Required Pipe Internal Diameter | mm | |
| Selected pipe size DN | mm | |
| Selected pipe size inch | Inch | |
| Water velocity in the pipe | m/s | |
| Flowrate | usgpm | |
| Maximum Allowable Frictional Loss | ft/100ft | |
| Min. Required Pipe Internal Diameter | Inch | |
| % tolerance to the imposed allowable friction loss* | % |
Input data
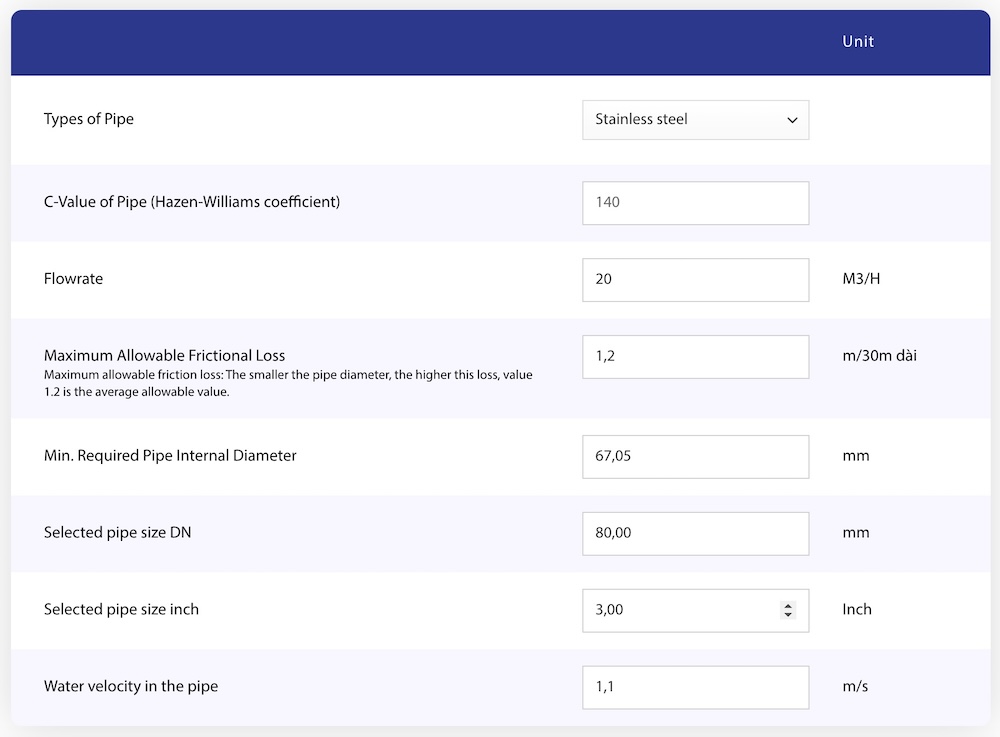
Step 1: Select the frame: Select the types of pipe, you need to choose the correct pipe material you are using to be able to access the corresponding C value. For example, choose stainless steel pipes
Step 2: Enter the water flow rate through the pipe, the unit is m3/h. For example, enter 20m3/h
Step 3: The maximum allowable friction loss frame, according to the above analysis, can be chosen in the range of 1,2-3,0. For example, choose 1,2
Result:
Step 4: Minimum required internal diameter to meet the flow rate with the selected loss. It is 67,05mm
Step 5: Suggest pipe diameter according to DN (mm). This recommendation for rounding up to even size is based on commonly available pipe sizes on the market. It is 80mm
Step 6: Suggest pipe diameter in Inches. This recommendation for rounding up to even size is based on commonly available pipe sizes on the market. It is 3inch
Step 7: Velocity of water flowing in the pipe in m/s, this value is appropriate in the range of 0,9-2,4. It is 1,1
Then the result will be as follows:
If you have questions about how to calculate pipe size, please contact our Company’s Sales department for more detailed instructions.