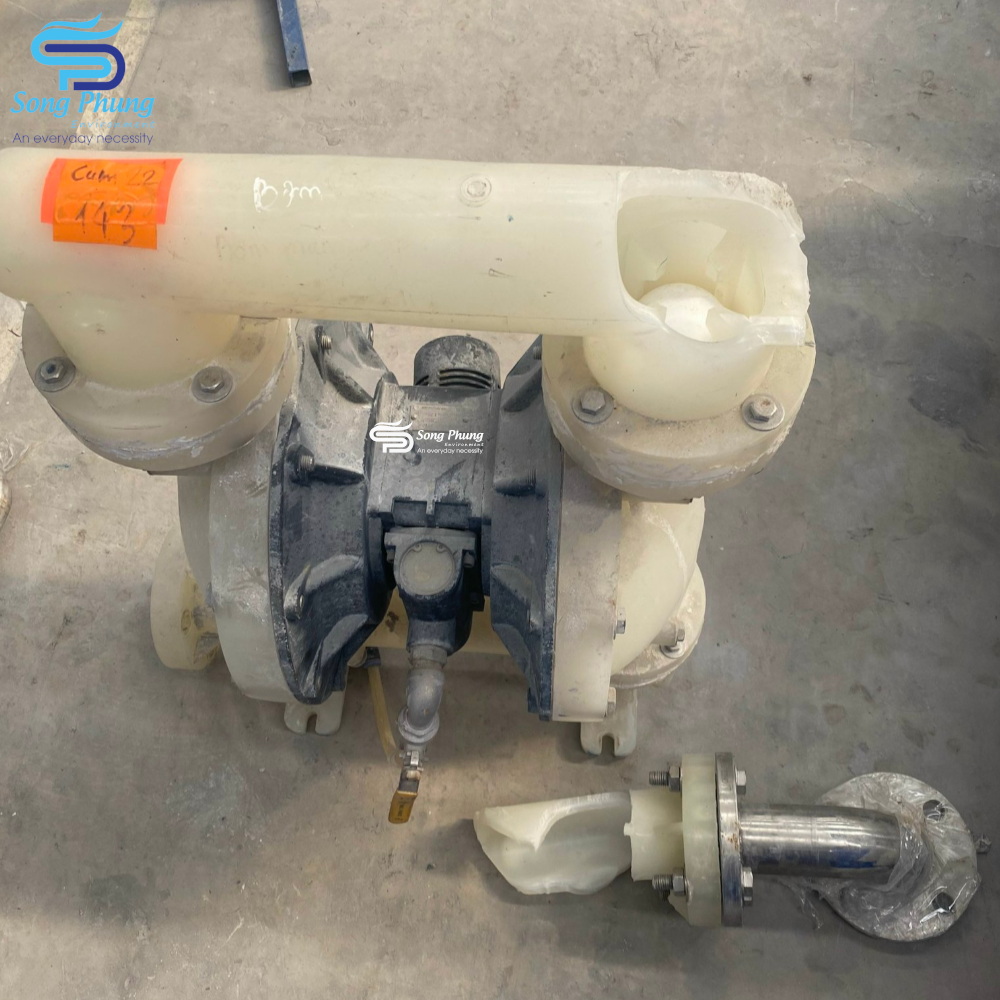
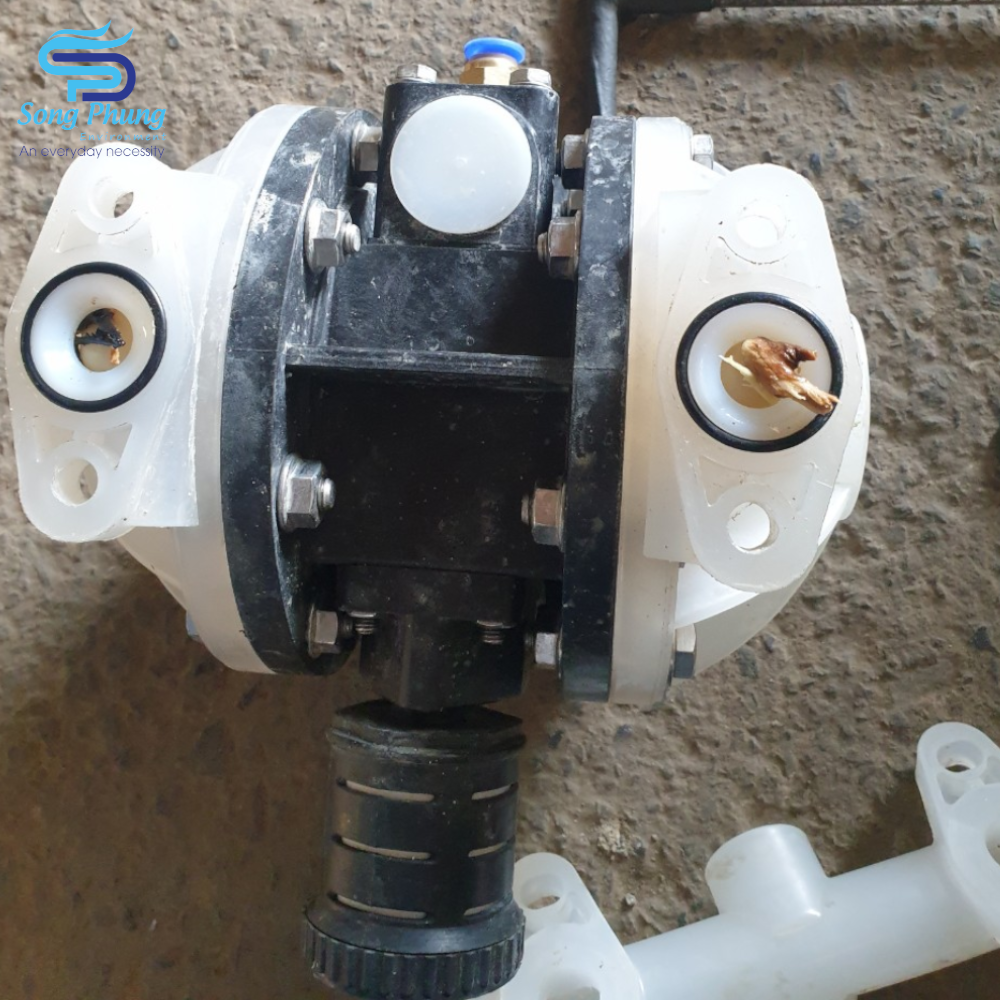
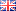
Pneumatic diaphragm pump repair service
Air operated diaphragm pumps are siphon type pumps driven by air pressure, with internal one-way ball valves that achieve performance through gravity and liquid pressure acting on the ball. When operating, the pump maintains a pressure higher than the external environment and is often used to transport chemical liquids.
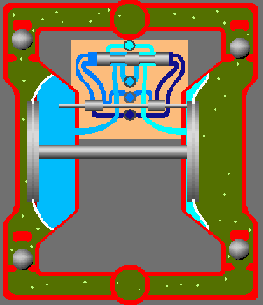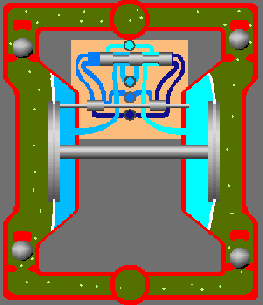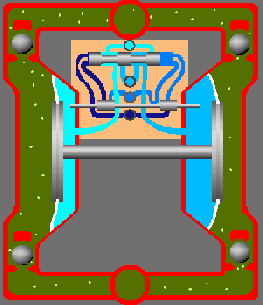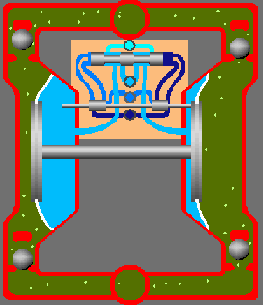
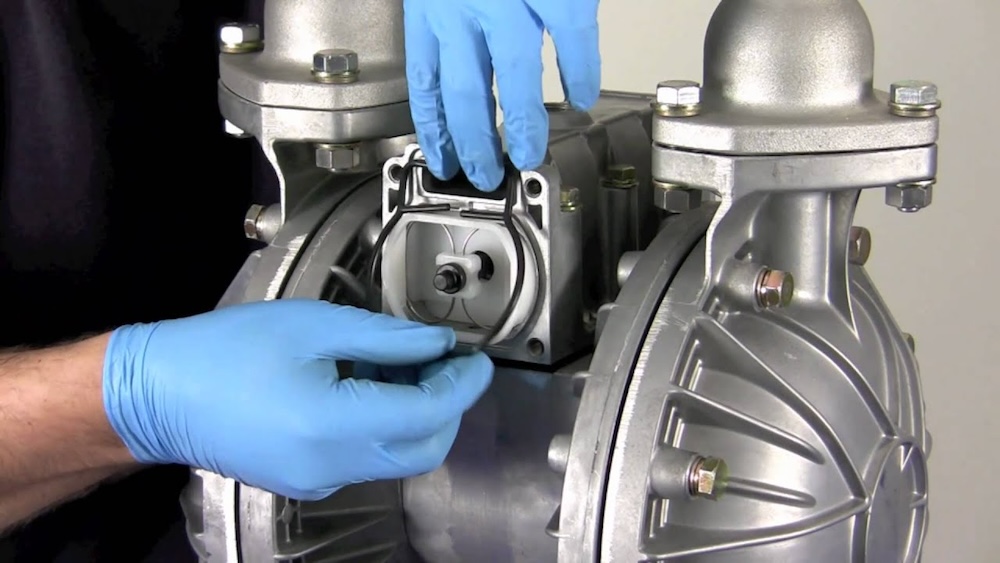
The pneumatic diaphragm pump begins to operate when the air distribution system directs the air supply to the right air chamber and the back of the diaphragm. This moves the diaphragm away from the center block and towards the liquid chamber, in the process pulling the opposite diaphragm inward. This means that the opposite diaphragm is now on the suction stroke. At the same time, atmospheric pressure pushes the liquid into the intake pipe, forcing the inlet valve ball off its seat. This allows the liquid to move past the inlet valve ball and into the liquid chamber.
During the operating life of any pumping equipment, periodic maintenance, servicing, repairs, and replacement of spare parts are inevitable. On the contrary, a well-planned maintenance schedule will prolong the life of the equipment and maintain its performance and operating efficiency.

Can I maintain, service, repair, clean, and replace diaphragm pump parts myself?
The answer is yes. However, the steps must be recorded on video and photos, because when you reassemble the accessories, you will have a basis for making sure that you install the accessories in the correct order and direction.
Furthermore, you need to have experience and knowledge of mechanics to be able to install the gaskets/seals without misalignment causing leakage and know how to retest the pump after completing the work and especially the necessary safety measures during the implementation process
Song Phung provides a full package of maintenance, service, repair, cleaning, and replacement of genuine diaphragm pump parts:
The service steps include details as listed below. During disassembly, the maintenance department must consider factors such as the residual pressure difference, the hazardous nature of the transported liquid itself, the tightness of the assembly, and the orientation of the components. The following are points to note and maintenance techniques when disassembling and maintaining pneumatic double diaphragm pumps:
1. Initial safety precautions:
Before disassembling the pump, the maintenance personnel should consider whether the transported liquid is hazardous. Be sure to take appropriate safety precautions, wear protective equipment, and prepare a first aid kit.
2. Releasing residual pressure:
Before disassembling the pneumatic double diaphragm pump, it is important to completely release the pressure inside the pump and pipeline. Pay attention to situations where the pump and pipeline may be clogged, as failure to completely release the pressure may result in the possibility of spraying and danger during disassembly. In such cases, be cautious during disassembly and take the necessary safety precautions. It is recommended to use a wrench to loosen the parts by hand a little to release the pressure, and wait until the liquid has completely drained before continuing to loosen a little more.
3. Screw Disassembly Technique:
It is recommended to loosen the screws by hand (#B-11) before using the pneumatic tool for disassembly. This helps to avoid the possibility of thread damage due to vibration when using the pneumatic tool directly. When tightening the screws, use a symmetrical sequence and tighten them in stages. Make sure that the coupling gaps are evenly sealed to avoid leakage or the possibility of pump body rupture due to uneven stress distribution.
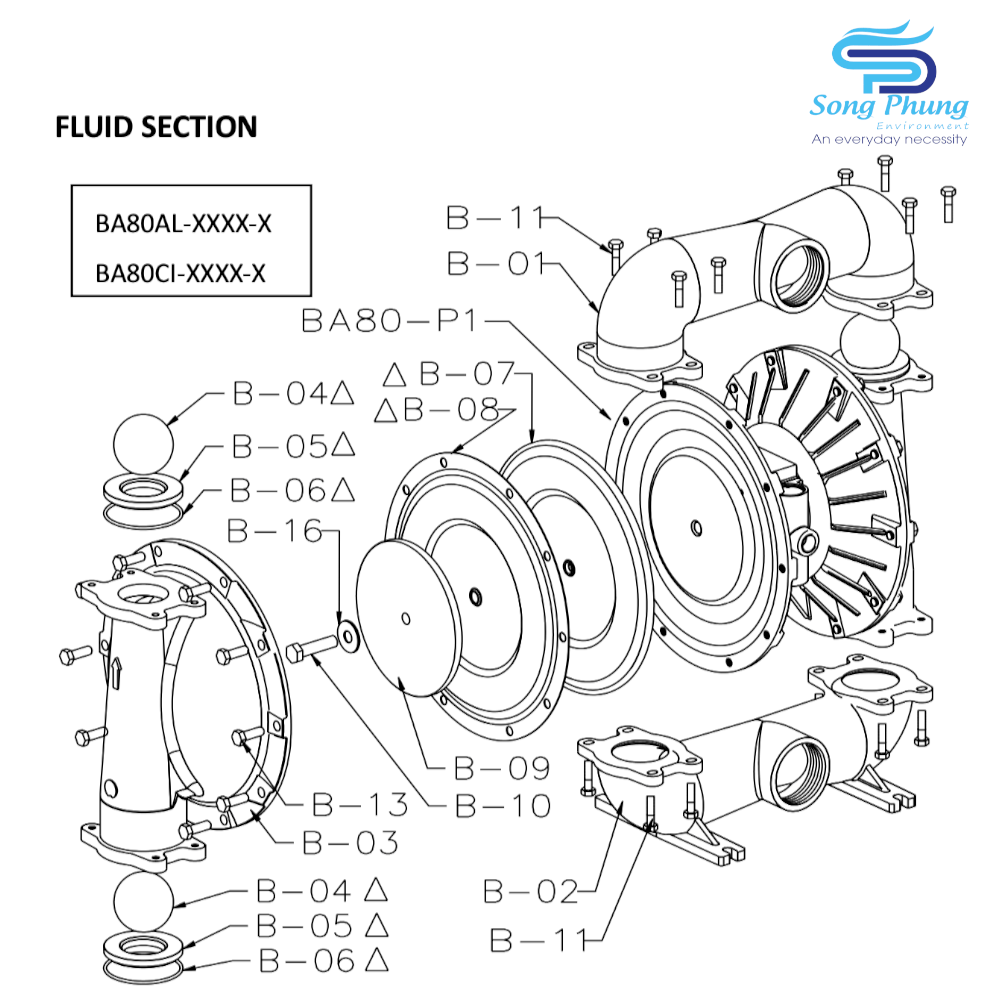
4. Pay attention to the assembly sequence and direction:
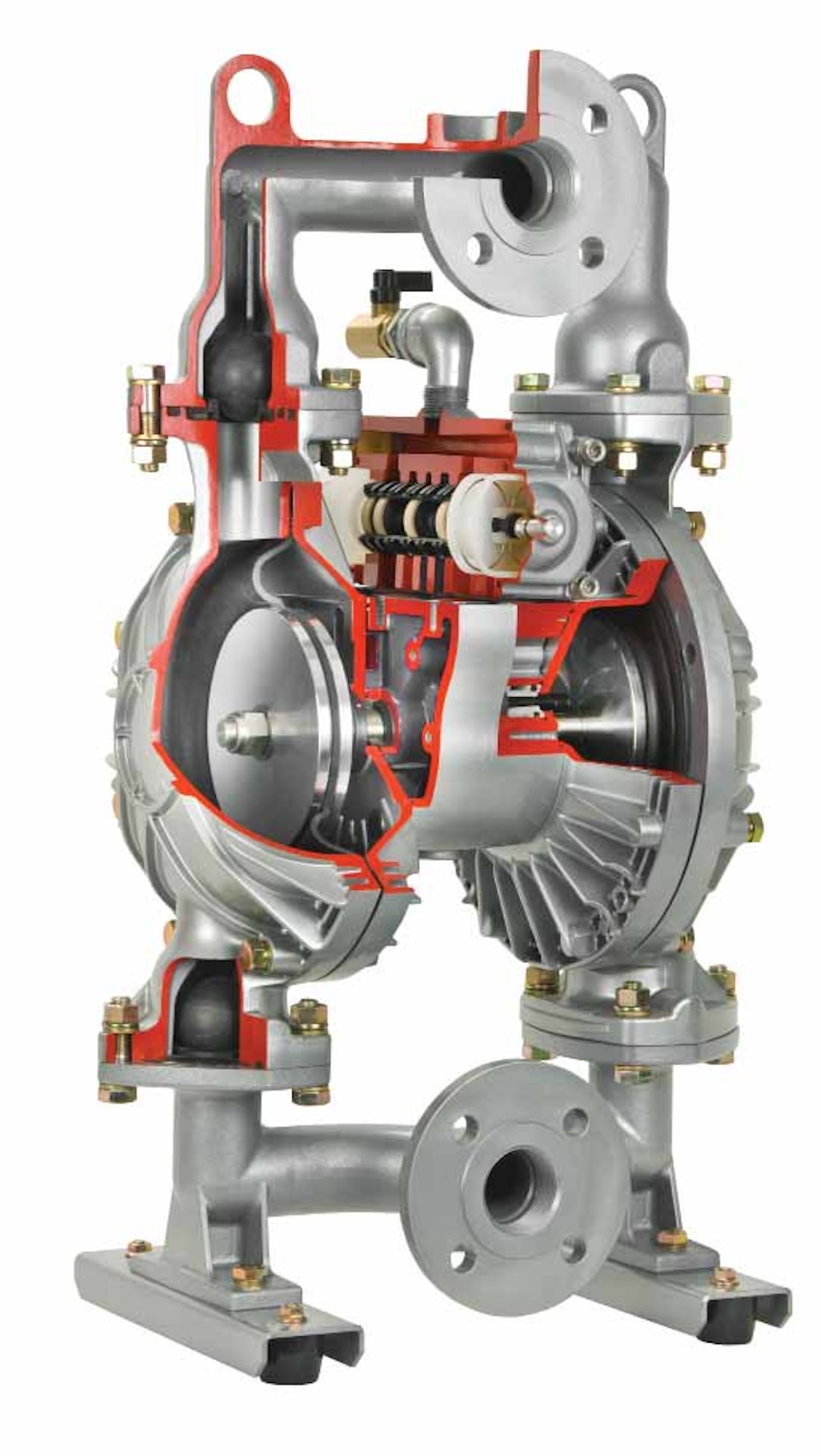
Some components in the pneumatic diaphragm pump have a fixed assembly sequence and direction. Improper assembly may cause the pump to malfunction or lead to abnormal fluid transport. Please refer to the disassembly diagram in the pump operating manual before disassembling and familiarize yourself with the assembly sequence and direction.
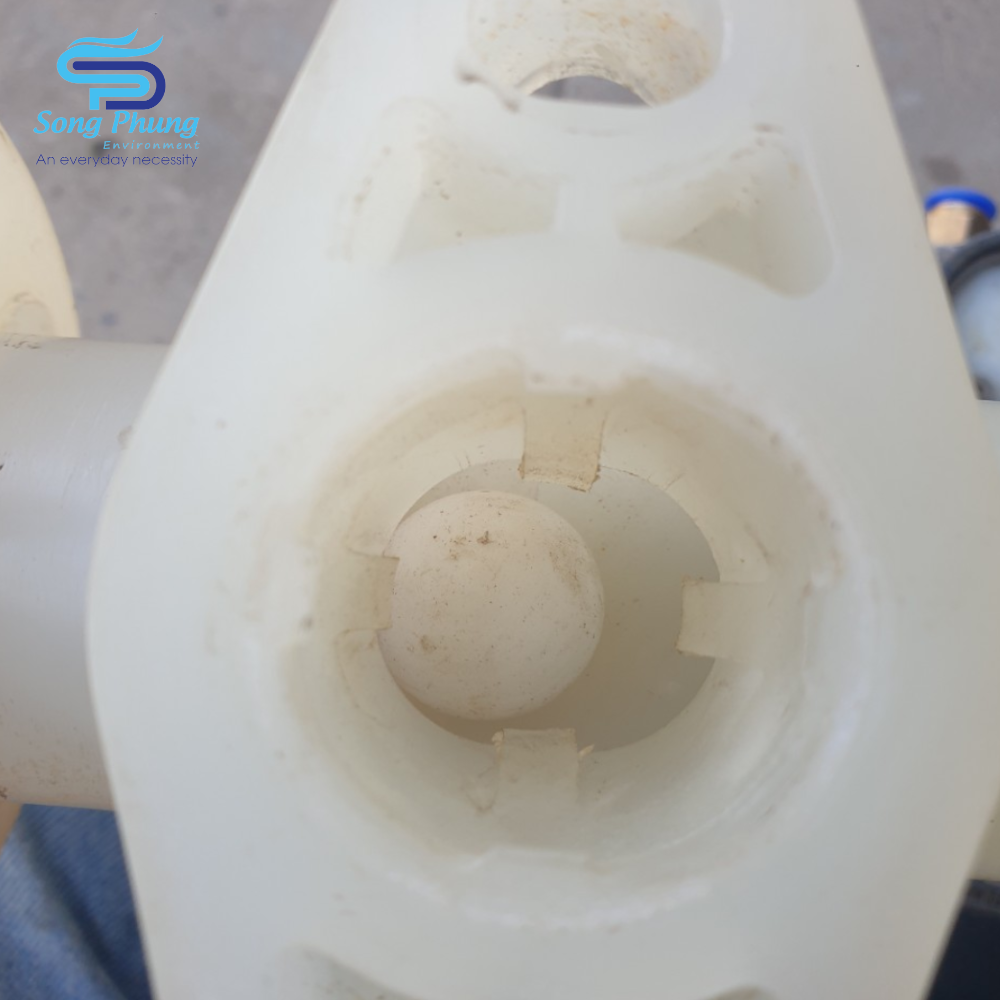
5. Maintenance of the inlet/outlet pipes and ball valve parts:
Check for any blockage or adhesion in the piping and ball valve parts (#B-04). Use appropriate cleaning tools or solvents to clean, taking care not to damage the ball valve and valve seat, which may affect the pump performance. If the ball valve, ball valve cover or ball valve seat are worn and lose roundness, they need to be replaced. In addition, for the pipe washer (#B-06), prepare a sharp screwdriver to disassemble and insert it from the bottom gap to lift it up. Since the PTFE gasket is easily deformed and lacks elasticity, it should be reinstalled in its original direction and position. If the deformation is too significant, resulting in loss of sealing effect, it should be replaced.
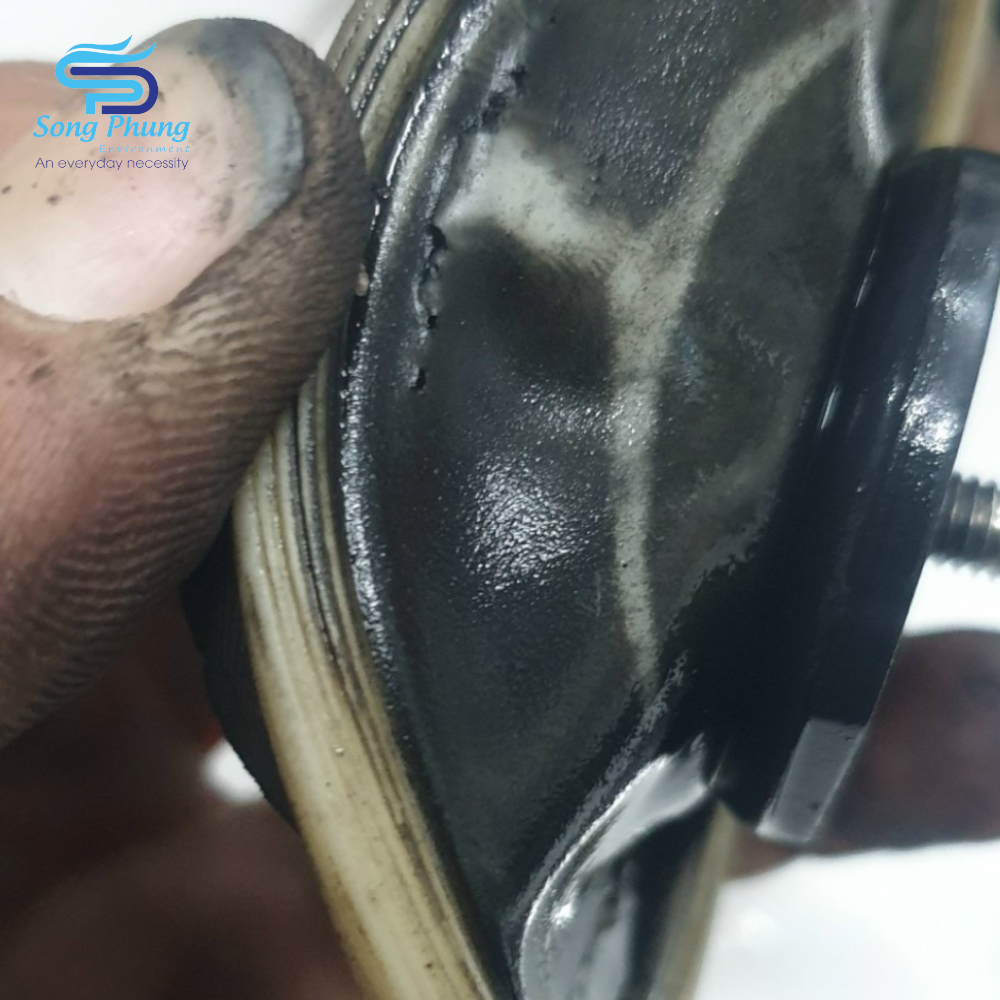
6. Check the diaphragm component:
The diaphragm liner (#B-07) and the diaphragm itself (#B-08) may be damaged or corroded due to the characteristics of the liquid. Check the elasticity or color change of the diaphragm to determine whether it should be replaced first. In addition, if the liquid contains impurities or sharp particles, the diaphragm may be dented, cut, or even broken under the force of reciprocating pressure. The diaphragm should be replaced regularly based on the conditions of use to prevent liquid from leaking into the air chamber, which may damage other components and increase maintenance costs.
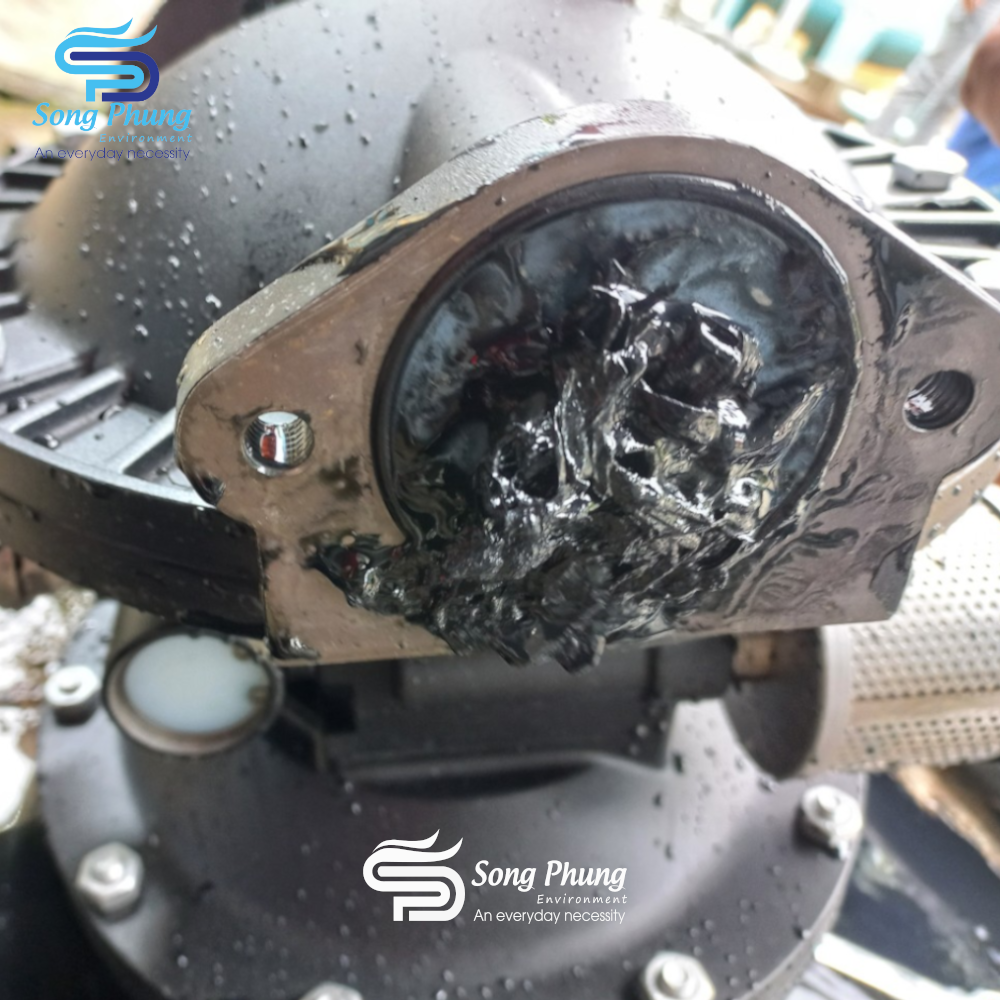
7. Maintenance of pneumatic valve (sequence valve):
After disassembly, clean the surface of the parts from any grease impurities. Next, check the gasket (#B-06) and the main parts of the air valve (#A-03/05/11/13/18/29/31) for any signs of wear. If there are any noticeable damages, dents or scratches, replace them immediately to avoid the pump from operating abnormally due to air leakage. If there are no problems, apply a thin layer of lubricant (pressure and temperature resistant grease) evenly to the gasket and the above-mentioned parts before assembling them in the correct order and direction.
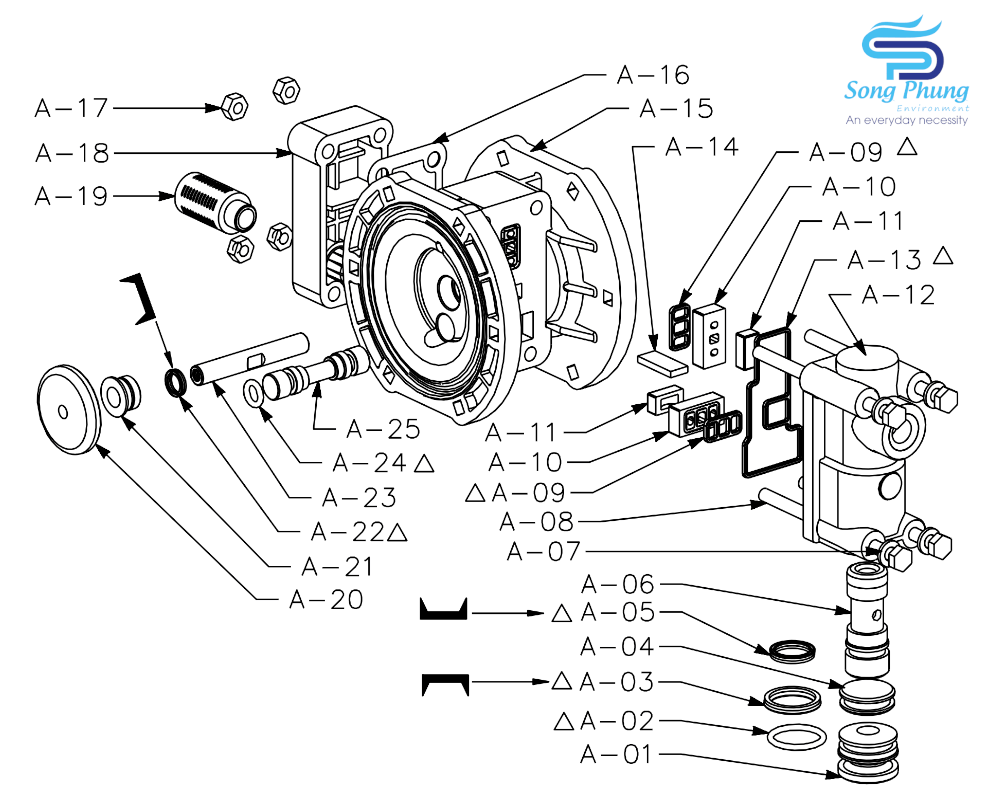
8. Maintenance of the pump air chamber:
After disassembling the diaphragm, check whether there is any oil contamination or water accumulation in the air chamber and clean it thoroughly. If liquid has entered the air chamber due to the diaphragm rupture, causing corrosion or blockage, the relevant components must be replaced in time.
9. Maintenance of the diaphragm shaft and switch valve components:
After disassembling, clean the surface of the components from any oil contamination. Then, check the seal ring, diaphragm shaft and switch valve components for any signs of wear. If there is any noticeable damage, dents or scratches, replace them immediately to avoid abnormal pump operation due to air leakage. If there is no problem, apply a thin layer of lubricating oil (pressure and temperature resistant grease) evenly to the seal ring and the above-mentioned components before assembling them in the correct order and direction.
10. Check the muffler:
If the air quality around the air compressor or pump is poor, check whether the muffler is seriously dirty and causes the air discharge pipe to be blocked. Avoid the pump malfunctioning or performance reduction due to insufficient discharge pipe.
11. Filter maintenance (garbage filter, air filter):
If the pump is equipped with a filter, regularly check and clean the filter to avoid clogging or damage.
12. About lubricating oil:
When applying lubricating oil to the parts, make sure that the right amount of oil is applied evenly to the surface. Avoid applying too much oil which may block the air passage and affect the normal operation of the pump.
13. Reassemble the pump and conduct a test run:
After reassembling the pump completely, it is necessary to conduct a test run of the pump with clean water. During the test operation, it is necessary to record a clip showing the parameters: Air inlet pressure, Air inlet flow, Water outlet pressure and Water outlet flow. These values should change from lowest to highest and from highest to lowest.
In summary, proper inspection and maintenance of pneumatic double diaphragm pumps are important steps to ensure smooth operation and prolong the life of the pump. By implementing these maintenance measures, pneumatic double diaphragm pumps can continue to operate effectively in a variety of applications, improving productivity and operating efficiency.
Please contact SongPhung via hotline for more accurate advice and quotes for your pump repair costs.